Last update: August 2, 2004
References in Computational Geometry on the reconstruction of surface meshes from point samples via surface propagation:
BibTeX references
15th Brazilian Symposium on Computer Graphics and Image Processing (SIBGRAPI),
pp. 179-186, Fortaleza-CE, Brazil, October 2002.
We present a fast and memory efficient algorithm that generates a manifold triangular mesh S passing through a set of unorganized points P in R³. Nothing is assumed about the geometry, topology or presence of boundaries in the data set except that P is sampled from a real manifold surface. The speed of our algorithm is derived from a projection-based approach we use to determine the incident faces on a point. Our algorithm has successfully reconstructed the surfaces of unorganized point clouds of sizes varying from 10,000 to 100,000 in about 3-30 seconds on a 250 MHz, R10000 SGI Onyx2. Our technique is especially suitable for height fields like terrain and range scan data even in the presence of noise. We have successfully generated meshes for scan data of size 900,000 points in less than 40 seconds.
M. Gopi, S. Krishnan, C. T. Silva
Computer Graphics Forum (EUROGRAPHICS 2000), 19(3), pages C467-C478.
We present a fast, memory efficient algorithm that generates a manifold triangular mesh S passing through a set of unorganized points P in R³. Nothing is assumed about the geometry, topology or presence of boundaries in the data set except that P is sampled from a real manifold surface. The speed of our algorithm is derived from a projection-based approach we use to determine the incident faces on a point. We define our sampling criteria to sample the surface and guarantee a topologically correct mesh after surface reconstruction for such a sampled surface. We also present a new algorithm to find the normal at a vertex, when the surface is sampled according our given criteria. We also present results of our surface reconstruction using our algorithm on unorganized point clouds of various models.
J. Huang and C. H. Menq
Computer-Aided Design
Volume 34, Issue 2 , February 2002, Pages 149-165
Web link:
In this paper, a novel approach is proposed to reliably reconstruct the geometric shape of a physically existing object based on unorganized point cloud sampled from its boundary surface. The proposed approach is composed of two steps. In the first step, triangle mesh structure is reconstructed as a continuous manifold surface by imposing explicit relationship among the discrete data points. For efficient reconstruction, a growing procedure is employed to build the 2-manifold directly without intermediate 3D representation. Local and global topological operations with ensured completeness and soundness are defined to incrementally construct the 2-manifold with arbitrary topology. In addition, a novel criterion is proposed to control the growing process for ensured geometric integrity and automatic boundary detection with a non-metric threshold. The reconstructed manifold surface captures the object topology with the built-in combinatorial structure and approximates the object geometry to the first order. In the second step, new methods are proposed to efficiently obtain reliable curvature estimation for both the object surface and the reconstructed mesh surface. The combinatorial structure of the triangle mesh is then optimized by changing its local topology to minimize the curvature difference between the two surfaces. The optimized triangle mesh achieves second order approximation to the object geometry and can serve as a basis for many applications including virtual reality, computer vision, and reverse engineering.
Author Keywords: Shape recovery; Surface reconstruction; Mesh optimization; Curvature estimation
Hong-Wei Lin, Chiew-Lan Tai, Guo-Jin Wang
Computer-Aided Design, 36(1): pp.1-9, January 2004.
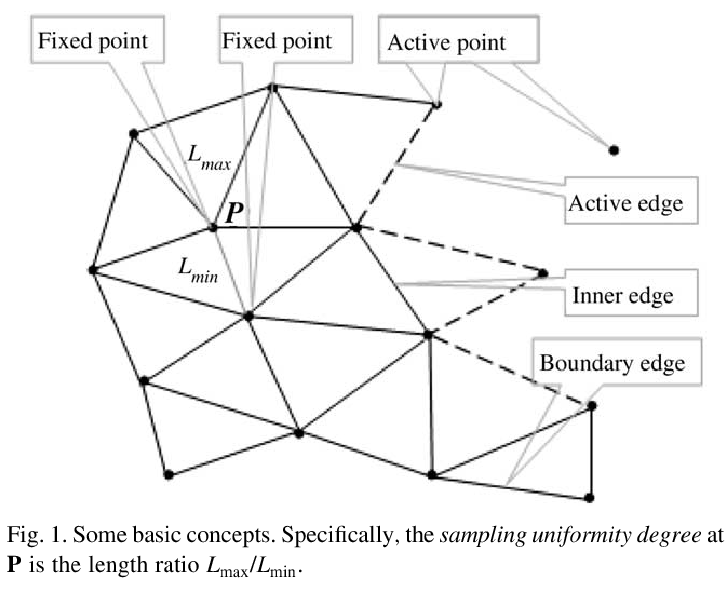
This paper presents an algorithm for reconstructing a triangle mesh surface from a given point cloud. Starting with a seed triangle, the algorithm grows a partially reconstructed triangle mesh by selecting a new point based on an intrinsic property of the point cloud, namely, the sampling uniformity degree. The reconstructed mesh is essentially an approximate minimum-weight triangulation to the point cloud constrained to be on a two-dimensional manifold. Thus, the reconstructed surface has only small topological difference from the surface of the sampled object. Topological correct reconstruction can be guaranteed by adding a post-processing step.
Author Keywords: Point cloud; Intrinsic property; Reconstruction

Page created & maintained by Frederic Leymarie, 2004.
Comments, suggestions, etc., mail to: leymarie@lems.brown.edu